IS it the first time that you are formatting the disk and ever did before?? Then, apart from the asking about the file system that the users want to use, if you are using the disk formatting tools, then the question arises regarding the “allocation unit size”.
If you are not aware of this, they know what actually it means and the value that you should set for it. Setting the right unit size of the allocation is very important when you are formatting a disk/drive.
So, as if you are not aware of this, you can read this post completely to know all those details. Here you can get the complete information about the allocation unit size and the related information to it. Let us first go into the details Allocation Unit Size means.
Contents
What does the Allocation Unit Size Mean??
Allocation Unit Size is also known as “Cluster size”. The cluster size here means the very small chunk of the space of the disk which holds or which is capable of holding a file.
When the sizes of the file do not come as the even multiples of the size of the cluster, additional space is to be allocated for holding up the file. When the cluster size is not specified while the users format the disk, the default size will be selected considering the partition size.
Windows select the defaults in order to reduce the disk space that has been lost as well as to decrease the fragmentation which occurs on the partition. So, know let us know about the disk formatting and the actual size allocated by default by windows and what allocation unit size you should allocate if you do it manually.
More about Allocation Unit Size in File Systems
When the users start formatting the partition in any of the file systems like FAT, NTFS, exFAT etc., by default windows will make use of the values set default if the disk formatting is done by using the command
“Format” from the command line without mentioning the size of the cluster or when the allocation unit box that belongs to the format dialogue box lists out the allocation size by default i.e., when the users format the disk from the windows explorer.
Don’t miss – Is watching copyrighted material online illegal?
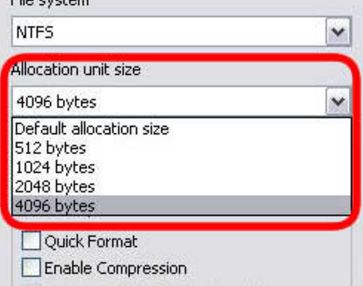
By default, if you are formatting into NTFS, the maximum cluster size under the Windows NT 4.0 and the windows next versions will be 4 KB. This is due to the reason that the NTFS files do not compress on those drives having the cluster size larger.
Unless and until the user overrides the default settings, this NTFS files conversion through the format command will not take larger cluster size than the default 4 KB. Users can do it either by giving the larger size for the cluster in the format dialogue box of the windows explorer.
If you are using the utility Convert.exe for converting the FAT partition into the NTFS file system, by default Windows will make use of the original cluster size of the FAT as the cluster size of the NTFS which is up to 4 KB.
But, if the cluster size of the FAT is more than the 4 KB, then it is converted to 4 KB cluster size in the NTFS. This is due to the reason that, structures of the FAT are aligned on the boundaries of the cluster and so the big cluster size is not allowed during the conversion. Check out the default cluster sizes for the NTFS from the Microsoft support page.
What is the Allocation Unit Size to Set??
It is always advisable for the users to set the allocation unit size smaller if there are many small files which help to save the space of the disk. But, if the size of the file is large then you can set the allocation size also larger. Doing this can increase the system performance.
The hard drives are partitioned into clusters and the allocation unit size that you assign will determine the actual size of the single cluster. The type of file system you format the hard drive will keep track of the clusters state. So, when a part of the file or when the complete file is written on the cluster it is considered as taken by it.
The speed of the hard drive will become slower when the cluster size is small. This is because every file that you write on the cluster will be broken into the small number of pieces and it will take some time for collecting all the broken file pieces back into one place and collect them as one. But, if the cluster size is big the space that is present on the disk is said to be wasted.
Finally, if you ask about what size should be set for allocation unit, there is no correct benchmark set for it. But it is recommended that, if the file size that you wanted to store on the hard drive is big then you can set the larger size of the cluster. Doing this will also improve the speed of the hard drive as well as its performance. And when you are trying to smaller file size, you can consider the cluster size also small.
Doing this will save the space of the disk or the drive. Note that, when you are formatting a disk or drive, if it is not done in a proper way or if there is any interruption during the process then your data of the drive will be lost. So, be careful while formatting the disk and while allocating the disk space.
Also note that, when you are formatting a disk partition under the Windows NT or the other windows versions 3.5, 3.51, and 4.0 Setup, the partition will be converted into the FAT at first and later on to NTFS. Doing this will keep the cluster size same as it is described earlier when a partition or drive is formatted in the Setup.
This is all about the Allocation and the Allocation Unit Size. Based on the information given here you can set the allocation unit size. Hope, the information is useful.